Noun Clauses As Direct Objects - in which sentence does a noun clause function as the ... - Therefore, both of these noun clauses are the subject of the sentence.
Noun Clauses As Direct Objects - in which sentence does a noun clause function as the ... - Therefore, both of these noun clauses are the subject of the sentence.. Nouns can function as subjects, direct objects, indirect objects, object of the preposition, and predicate nominatives. The noun clause is a clause that functions like a noun in the sentence. These are examples of nominal clauses (sometimes called 'noun clauses'): They can act as the subject, a direct or indirect object, a predicate noun, an adjective complement, or the object of a preposition. Noun clauses can function as subjects, objects, or complements.
Feb 12, 2020 · active and passive clauses direct objects are always noun phrases (or their equivalents, e.g., nominal clauses). There are three types of objects. Subjects, direct objects, indirect objects, objects of the preposition, and subject complements. Jul 01, 2013 · noun clauses are a type of dependent clause that perform nominal functions. A noun clause is a clause that functions as a noun.
In grammar, a direct object is a word, phrase, or clause that follows and receives the action of a transitive verb.
The teacher is direct object) the teacher was hated by everybody. Remember that a noun names a person, place, thing, or idea. I know that the students studied their assignment. Noun clauses can act as subjects, direct objects, indirect objects, predicate nominatives, or objects of a preposition. Become comfortable with the concept by reading through this helpful guide! Objects are words that 'receive' another part of a sentence. A noun clause is a clause that functions as a noun. Jan 21, 2020 · nominal clauses as direct objects all sentences, then, are clauses, but not all clauses are sentences. Jun 12, 2021 · noun clauses are dependent clauses that can replace any noun in the sentence: Feb 12, 2020 · active and passive clauses direct objects are always noun phrases (or their equivalents, e.g., nominal clauses). There are three types of objects. They can act as the subject, a direct or indirect object, a predicate noun, an adjective complement, or the object of a preposition. This page has lots of examples of noun clauses and an interactive exercise.
In grammar, a direct object is a word, phrase, or clause that follows and receives the action of a transitive verb. Like all clauses, a noun clause has a subject and a verb. Because of this, noun clauses can perform all the roles that a normal noun would fill in a sentence: They can act as the subject, a direct or indirect object, a predicate noun, an adjective complement, or the object of a preposition. Noun clauses can function as subjects, objects, or complements.

Subjects, direct objects, indirect objects, objects of the preposition, and subject complements.
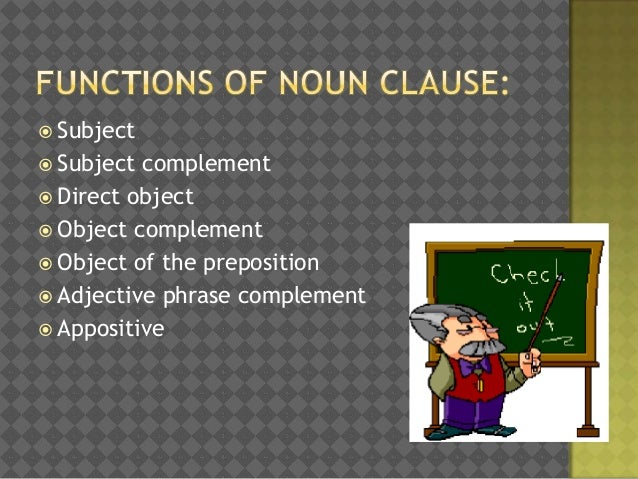
In all, there are five different functions that a noun clause can serve: Noun clauses begin with words such as how, that, what, whatever, when, where, whether, which, whichever, who, whoever, whom, whomever, and why. Feb 12, 2020 · active and passive clauses direct objects are always noun phrases (or their equivalents, e.g., nominal clauses). They can act as the subject, a direct or indirect object, a predicate noun, an adjective complement, or the object of a preposition. Therefore, both of these noun clauses are the subject of the sentence. Jan 21, 2020 · nominal clauses as direct objects all sentences, then, are clauses, but not all clauses are sentences. These are examples of nominal clauses (sometimes called 'noun clauses'): There are three types of objects. A noun clause may have you questioning your grammar knowledge. The noun clause is a clause that functions like a noun in the sentence. Noun clauses can function as subjects, objects, or complements. Jun 12, 2021 · noun clauses are dependent clauses that can replace any noun in the sentence: Nouns can function as subjects, direct objects, indirect objects, object of the preposition, and predicate nominatives.
Become comfortable with the concept by reading through this helpful guide! In addition to nouns and pronouns , noun clauses also perform the grammatical function of direct object. Jan 21, 2020 · nominal clauses as direct objects all sentences, then, are clauses, but not all clauses are sentences. Remember that a noun names a person, place, thing, or idea. Noun clauses can act as subjects, direct objects, indirect objects, predicate nominatives, or objects of a preposition.
There are three types of objects.
Noun clauses begin with words such as how, that, what, whatever, when, where, whether, which, whichever, who, whoever, whom, whomever, and why. Noun clauses can act as subjects, direct objects, indirect objects, predicate nominatives, or objects of a preposition. Feb 12, 2020 · active and passive clauses direct objects are always noun phrases (or their equivalents, e.g., nominal clauses). Jan 21, 2020 · nominal clauses as direct objects all sentences, then, are clauses, but not all clauses are sentences. There are three types of objects. Remember that a noun names a person, place, thing, or idea. Noun clauses can function as subjects, objects, or complements. In addition to nouns and pronouns , noun clauses also perform the grammatical function of direct object. In grammar, a direct object is a word, phrase, or clause that follows and receives the action of a transitive verb. Objects are words that 'receive' another part of a sentence. Subjects, direct objects, indirect objects, objects of the preposition, and subject complements. Jun 12, 2021 · noun clauses are dependent clauses that can replace any noun in the sentence: Because of this, noun clauses can perform all the roles that a normal noun would fill in a sentence:
The noun clause is a clause that functions like a noun in the sentence noun clauses. A noun clause may have you questioning your grammar knowledge.